2022-12-22
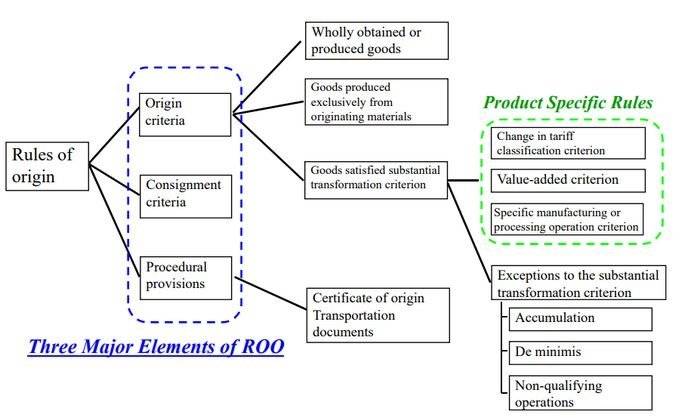
Rules of origin are the criteria needed to determine the national origin of a product, the importance of which is that tariffs and restrictions depend on the source of the import.
The practice of governments with regard to the rules of origin varies considerably. In a globalized world, it has become even more important for member countries to achieve a degree of harmonization in the implementation of this requirement.
Rules of origin determine the country in which a product is sourced or manufactured - its 'economic nationality' - and help to ensure that customs authorities correctly apply lower tariffs to the benefit of businesses. It is therefore vital to know where your products come from.
For example, certain goods are granted duty-free or reduced tariff treatment under the rules of origin of the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA). The rules of origin for trade agreements may seem daunting at first glance, but once you understand the basics, it is so simple.
Different countries determine the country of origin rules in different ways. For example, in the United States, CBP will use a number of different rules to determine the country of origin, including the "wholly produced" rule, the "de minimis" rule, and the "substantial transformation" rule. Other countries will apply other rules, and many trade agreements provide criteria and procedures for determining the country of origin.
Wholly obtained
Wholly obtained products are goods obtained exclusively in the territory of the FTA Contracting Party, without the addition of any non-original materials. It refers to live animals born and raised there, mineral products extracted from the ground, foodstuffs grown and harvested in the territory of the Contracting Party (e.g., fruit, cereals).
Substantial transformation
Substantive transformation is a rule of origin that requires goods to undergo a certain process in order to be considered as originating in a particular country. It has three different ways of expression.
Tariff classification change: a rule that requires a change in the HS classification of a non-originating material in order to obtain origin status.
Value-added calculations: rules that require a percentage of the total value of the final product to be added in the FTA area.
These rules can be expressed in two ways, as a maximum allowance for non-original inputs or a minimum requirement for local content.
- Specific processing: rules requiring specific processing at a particular stage of the production process.
These three types of substantial transformation can be used in combination with each other. Furthermore, within each of the three types, different types of exceptions and allowances can be used. They can specify parts of the rules that apply only to certain categories of products and allow for the relaxation of rule elements under special conditions.
Rules of origin are used in the following situations:
Measures and instruments to implement commercial policy, such as anti-dumping duties and safeguards.
To determine whether imported products should receive most-favoured-nation or preferential treatment.
For the purpose of trade statistics.
To apply labeling and marking requirements
For government procurement.
The two terms are similar in that they have the word "origin". However, they are very different.
Rules of origin are declared to customs at the time of importation and are used as a criterion for determining where a product was manufactured from. For example, a product may not have been produced entirely in a particular country, but rules of origin help to identify one country as the country of origin for this product.
A certificate of origin, on the other hand, is a document used to show the country of origin of the goods, containing details of the product, its final destination and the country of export.
This document is used as a reference for the imposition of import duties on the goods and to determine whether the goods are eligible for importation. It can be in hard or soft copy.
Note that the certificate of origin is issued after the rules of origin. The purpose is to certify that the goods comply with the rules of origin and that the goods meet certain criteria to be considered as originating in a particular country.

A certificate of origin proves where goods originated and is often needed for international trade, helping to determine taxes, tariffs, and quotas.
2022-11-04

Are you curious about how import duties and taxes are calculated? Then, JIKEship takes you to step by step to understand duties and taxes.
2022-11-24
We use third-party cookies in order to personalise your experience.
Read our cookie policy